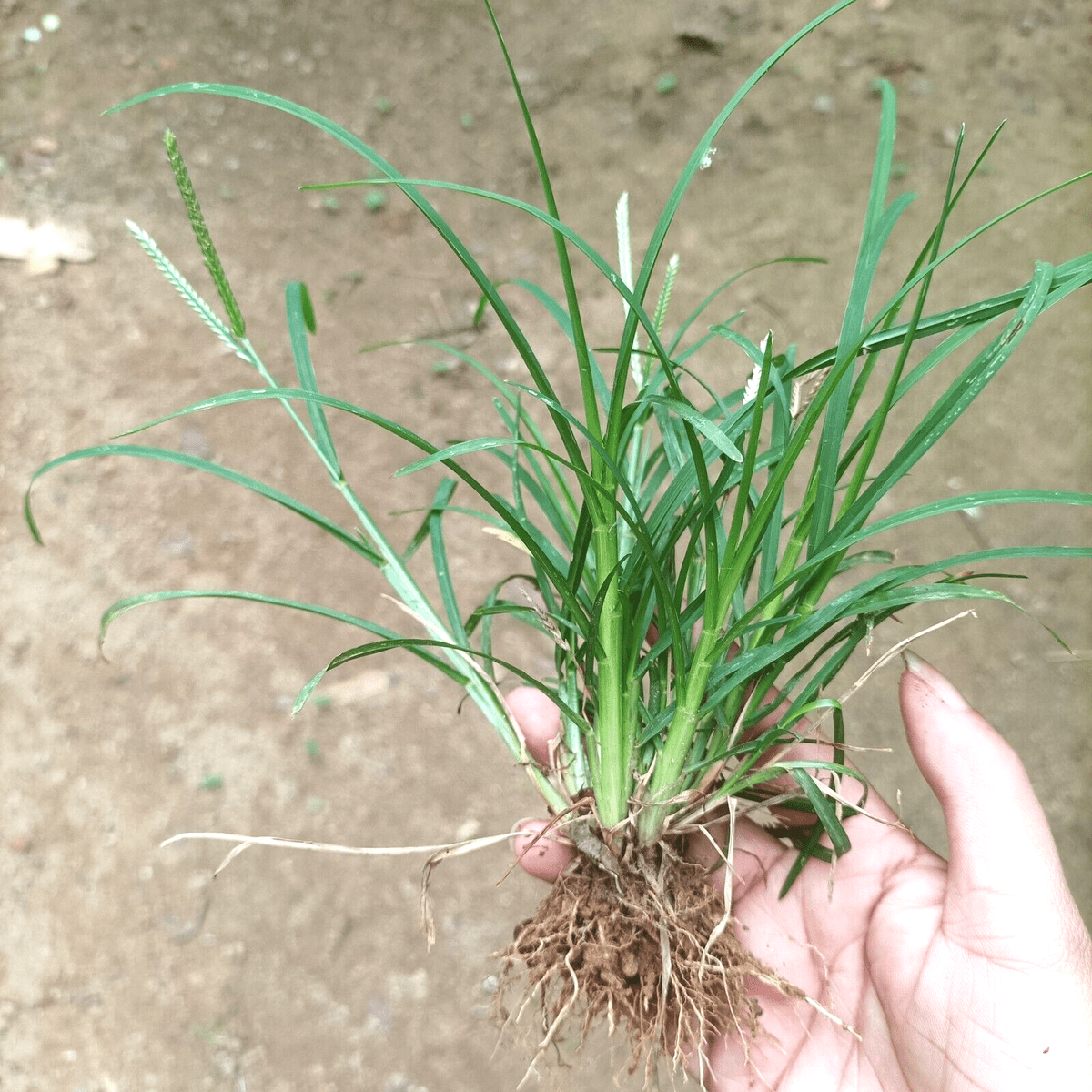
Goosegrass, scientifically known as $\text{Eleusine indica}$ and also called Wiregrass or Indian Goosegrass, is globally notorious as a pervasive weed. However, in traditional medicine across Asia, Africa, and South America, this resilient plant is a valuable natural remedy. Its potent healing properties stem from a rich phytochemical profile, including flavonoids, alkaloids, terpenoids, and saponins.
Here are 20 documented traditional uses and scientifically supported benefits of $\text{Eleusine indica}$ and how it is typically used:

Top 20 Benefits (Traditional & Scientific)
Systemic Health & Detoxification
- Diuretic Action: Traditionally used as a strong diuretic to promote urine production and treat urinary retention and oliguria (low urine output).
- Kidney Health: Used for supporting kidney function and treating various kidney problems, including kidney stones ($\text{anti-urolithiasic}$ properties).
- Antihypertensive: Scientific studies support its use in lowering high blood pressure by promoting diuresis and inhibiting $\text{ACE}$ (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme).
- Febrifuge: Used traditionally to reduce fever and body temperature.
- Influenza/Flu Tonic: Employed as a tonic to treat the symptoms of $\text{influenza}$ and the common cold.
- Hepatoprotective: Exhibits effects that protect the liver from oxidative damage and is used in traditional medicine for liver complaints.
- Antioxidant Power: Rich in phytochemicals that function as potent antioxidants, scavenging free radicals and reducing cellular $\text{oxidative}$ $\text{stress}$.
- Antidiabetic: Traditional use and preliminary studies suggest potential antidiabetic properties.
Pain, Inflammation, and Immunity
- Anti-inflammatory: Possesses powerful $\text{anti-inflammatory}$ properties to relieve swelling and inflammation.
- Analgesic: Used as a natural $\text{analgesic}$ to relieve general pain.
- Antiarthritic/Rheumatism: Traditional remedy for treating arthritis and joint pain.
- Antimicrobial: Demonstrates activity against various bacteria (including some resistant strains) and fungi, supporting its use against infections.
- Antiviral: Possesses antiviral properties, contributing to its use in flu and fever treatment.
- Anthelmintic: Used to expel worms from the intestine (anti-helminthic).
- Cytotoxic: Extracts have shown $\text{cytotoxic}$ properties, leading to exploratory research in anti-cancer potential.
Digestive and Topical Uses
- Gastrointestinal Health: Used to treat issues like diarrhea and dysentery due to its astringent and antimicrobial effects.
- Laxative: The plant (especially the root) is traditionally considered a laxative to promote bowel movements.
- Wound Healing: Applied topically to ulcers and to promote the healing of wounds.
- Skin Infections: Used topically in some regions to treat skin diseases and infections like ringworm.
- Post-Partum Aid: In some traditional practices, leaf juice is used to hasten the discharge of the afterbirth (placenta delivery) after childbirth and relieve pain from vaginal bleeding.
How Eleusine indica is Traditionally Used

The preparation and use vary widely depending on the region and the ailment being treated. The most common methods are:
- Decoction (Tea): The most frequent preparation involves boiling the whole plant (or just the aerial parts/roots) in water to create a concentrated liquid. This decoction is drunk to treat fever, hypertension, urinary problems, and internal infections.
- Infusion (Tonic): Fresh leaves are steeped in hot water to create a mild infusion, often used as a tonic for flu-related symptoms.
- Topical Poultice/Scrub: The fresh leaves are crushed or pounded to extract the juice or create a paste, which is then applied directly to affected areas to treat skin infections, wounds, or inflammation.
- Juice: The fresh juice from the crushed leaves is sometimes consumed directly for specific ailments like hastening afterbirth discharge.
Safety Warning: $\text{Eleusine indica}$ is primarily used in traditional and folk medicine. Due to potential interactions, toxicity concerns, and the need for standardized dosages, you should always consult a qualified healthcare practitioner or medical professional before using this plant for any medicinal purpose, especially if you have pre-existing conditions or are taking conventional medications.