The liver is the body’s largest internal organ, responsible for over 500 vital functions, including detoxifying the blood, metabolizing fats, and producing bile. While the term “detox” often implies a short-term cleanse, the real secret to a healthy liver is consistently providing it with the right $\text{antioxidants}$, $\text{healthy}$ $\text{fats}$, and $\text{fiber}$ through a balanced diet.
Here are 12 scientifically supported superfoods that enhance liver function, reduce fat accumulation, and fight inflammation.
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Superstars
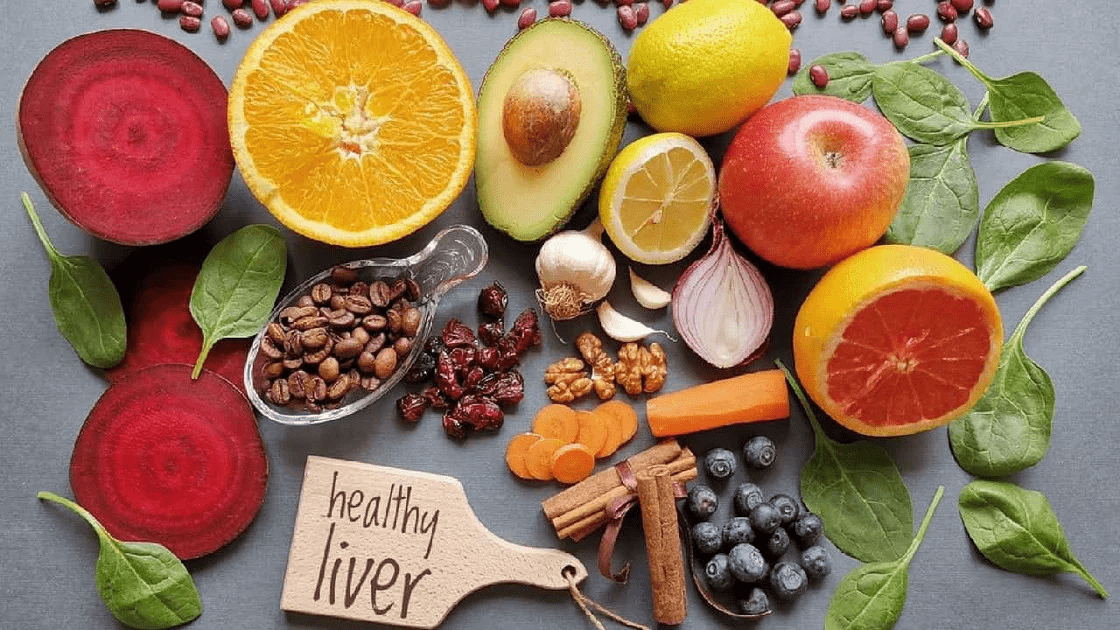

These foods are packed with compounds that protect liver cells from damage caused by toxins and free radicals.
- Coffee: Studies consistently show that drinking two to three cups of coffee per day protects the liver from disease, reducing the risk of $\text{fibrosis}$ (scarring) and $\text{cirrhosis}$. Its compounds prevent fat accumulation and boost the antioxidant glutathione.
- Green Tea: Contains high levels of catechins, powerful $\text{antioxidants}$ that have been linked to improved liver enzyme levels and a reduced risk of liver cancer. Brew it hot to maximize the $\text{catechin}$ content.
- Grapefruit: Rich in $\text{naringenin}$ and $\text{naringin}$, two $\text{antioxidants}$ that help reduce inflammation and protect liver cells from damage. They may also help activate liver enzymes that flush out toxins.
- Blueberries and Cranberries: These berries are packed with anthocyanins, which provide strong $\text{anti-inflammatory}$ and $\text{antioxidant}$ effects, and may help slow the progression of liver $\text{fibrosis}$.
- Garlic: Contains $\text{allicin}$, an active compound that helps reduce $\text{LDL}$ cholesterol and may reduce liver fat and improve enzyme levels, particularly in those with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease ($\text{MASLD}$).
Fat, Fiber, and Detoxification Support

These foods provide the essential building blocks and structural support the liver needs to metabolize fats and detoxify efficiently.
- Cruciferous Vegetables: $\text{Broccoli}$, $\text{Brussels}$ $\text{sprouts}$, and $\text{cauliflower}$ are rich in $\text{glucosinolates}$, which help activate the liver enzymes responsible for flushing out $\text{carcinogens}$ and other harmful substances.
- Leafy Greens: $\text{Spinach}$, $\text{kale}$, and other greens are a top source of glutathione, a major $\text{antioxidant}$ that plays a central role in the liver’s detoxification process.
- Oatmeal/Whole Grains: Provides complex carbohydrates and high amounts of $\text{fiber}$ that help you feel full, manage weight, and stabilize blood sugar—all crucial for reducing fat buildup in the liver.
- Walnuts: These are one of the best plant sources of $\text{omega-3}$ $\text{fatty}$ $\text{acids}$ and $\text{glutathione}$. Regular consumption has been linked to improved liver function tests in people with $\text{MASLD}$.
- Fatty Fish: $\text{Salmon}$, $\text{sardines}$, and $\text{mackerel}$ are rich in $\text{omega-3}$ $\text{polyunsaturated}$ $\text{fatty}$ $\text{acids}$. These healthy fats have been shown to reduce liver fat content and improve blood markers of liver health.
- Avocados: Packed with healthy $\text{monounsaturated}$ $\text{fats}$ and $\text{fiber}$, $\text{avocados}$ contain compounds that may help slow down liver damage and support overall weight management.
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil ($\text{EVOO}$): Using $\text{EVOO}$ instead of saturated fats helps reduce fat accumulation in the liver. Aim for $1-2 \text{ tablespoons}$ daily, which can be drizzled over salads or used for cooking.